Reflow ovens play a crucial role in electronics manufacturing. These ovens ensure precise soldering of components onto printed circuit boards. Oxidation problems pose significant challenges during the soldering process. Oxidation affects the quality and reliability of electronic connections. Addressing oxidation issues is essential for maintaining the integrity of electronic devices. Manufacturers rely on reflow ovens to tackle these problems effectively. Proper use of reflow ovens minimizes oxidation, enhancing the performance of electronic products.
Understanding Oxidation in Electronics Manufacturing
What is Oxidation?
Definition and Chemical Process
Oxidation involves a chemical reaction where a material loses electrons. This process often occurs when metals react with oxygen, forming metal oxides. In electronics manufacturing, oxidation can occur on metal surfaces exposed to air. The presence of oxygen leads to the formation of an oxide layer.
Impact on Electronic Components
Oxidation significantly impacts electronic components. Metal oxides form insulating layers that hinder electrical conductivity. This effect compromises the functionality of electronic devices. The reliability of solder joints decreases due to oxidation. Manufacturers must address oxidation to ensure product quality.
Common Oxidation Problems
Formation of Oxides on Metal Surfaces
Oxides form on metal surfaces during the soldering process. Exposure to air accelerates this formation. The oxide layer prevents proper solder adhesion. This issue affects the integrity of solder joints. Effective measures are necessary to prevent oxide formation.
Effects on Solderability and Electrical Connections
Oxidation reduces solderability by creating barriers on metal surfaces. Poor solderability leads to weak electrical connections. These weak connections result in device failures. The Vapour Phase Soldering Process offers a solution by displacing oxygen with vapor. This method ensures even heat distribution and minimizes oxidation. Addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining reliable electronic products.
Role of Reflow Ovens in Tackling Oxidation
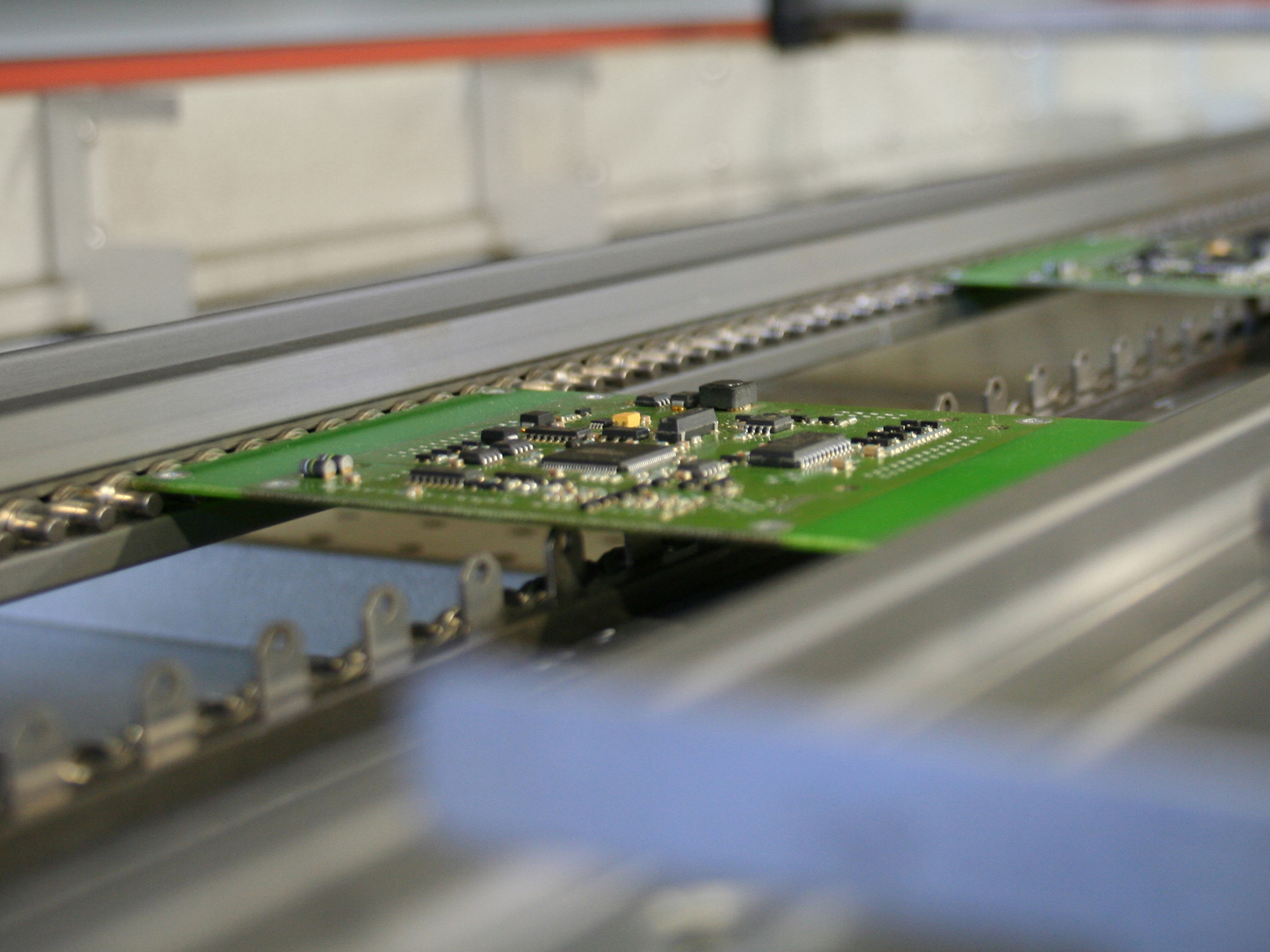
How Reflow Ovens Work
Basic Principles of Operation
Reflow ovens operate using convection heating. This method circulates air throughout chambers, ensuring even heat distribution around circuit boards. The process involves multiple zones within the oven. Each zone maintains a specific heat profile. This setup allows precise control over the soldering process. The uniform heat application is crucial for effective soldering.
Temperature Profiles and Control
Temperature control is vital in reflow ovens. Each assembly requires a unique reflow profile. Factors such as component type and board material influence these profiles. The reflow process must reach the correct temperature without damaging components. Lead-free assemblies demand even more precision due to narrower temperature ranges. Proper profiling ensures consistent and reliable solder joints.
Techniques to Minimize Oxidation
Use of Inert Atmospheres
Reflow ovens often use inert atmospheres to combat oxidation. Nitrogen is a common choice for this purpose. The inert gas displaces oxygen in the oven environment. This reduction in oxygen minimizes oxide formation on metal surfaces. Manufacturers achieve higher quality solder joints with this technique.
Flux Application and Its Role
Flux plays a crucial role in reflow ovens. The application of flux removes oxides from metal surfaces. This cleaning action improves solderability. Flux also protects surfaces from further oxidation during heating. The combination of flux and controlled atmospheres enhances the reliability of electronic connections.
Case Studies and Examples
Successful Implementation of Reflow Ovens
Case study 1: Shenzhen Chuxin Electronic Equipment Co., Ltd.
Shenzhen Chuxin Electronic Equipment Co., Ltd. implemented a lead-free nitrogen type hot air reflow oven. The company aimed to reduce oxidation during the soldering process. The reflow oven utilized a nitrogen atmosphere. This setup minimized oxygen exposure. The company achieved superior solder joint quality. The implementation resulted in enhanced reliability of electronic components. The reflow oven met the rigorous demands of modern electronics manufacturing.
Case study 2: Industry-wide adoption of lead-free soldering
The electronics industry adopted lead-free soldering practices. Manufacturers faced challenges with oxidation. Reflow ovens played a crucial role in this transition. The ovens provided precise temperature control. The use of inert atmospheres reduced oxide formation. The industry saw an improvement in solder joint integrity. Lead-free soldering became the standard due to environmental regulations. The adoption demonstrated the effectiveness of reflow ovens in tackling oxidation problems.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Key takeaways from case studies
The case studies highlighted the importance of controlled environments. Nitrogen atmospheres proved effective in reducing oxidation. Precise temperature control ensured consistent soldering results. The use of advanced reflow ovens improved product quality. Manufacturers benefited from enhanced reliability of electronic devices.
Recommendations for manufacturers
Manufacturers should invest in advanced reflow ovens. The use of nitrogen atmospheres is recommended. Temperature profiling must be precise. Regular maintenance of equipment ensures optimal performance. Training for operators enhances the effectiveness of reflow ovens. Manufacturers should prioritize addressing oxidation issues. The focus on quality leads to better electronic products.
Addressing oxidation in electronics manufacturing is crucial for ensuring the reliability of electronic components. Oxidation creates non-solderable oxides, affecting the quality of solder joints. Reflow ovens effectively tackle these issues by utilizing optimal reflow profiles and nitrogen atmospheres. Nitrogen reduces oxidation, enhancing solderability. Manufacturers achieve superior solder joint quality through precise temperature control. Investing in advanced reflow ovens leads to improved product performance. The adoption of these technologies reflects a commitment to producing high-quality electronic devices.
